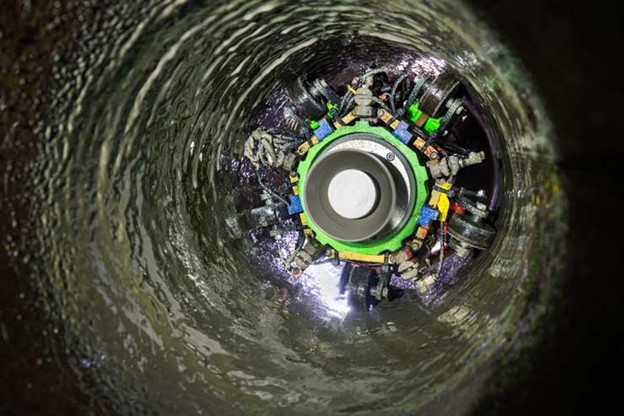
Framatome’s spray liner rehabilitates buried piping and underground components. (Photo: Framatome)
Framatome was recently awarded a multimillion-dollar contract to perform mitigation of buried condenser feed pipes at a three-unit nuclear power plant in the United States.
The France-based nuclear company plans to install spray-in-place structural pipe liner to mitigate more than one mile of large diameter underground piping connected to plant condenser boxes. The project will be performed during nine outages over eight years, with the first application planned for fall 2025.
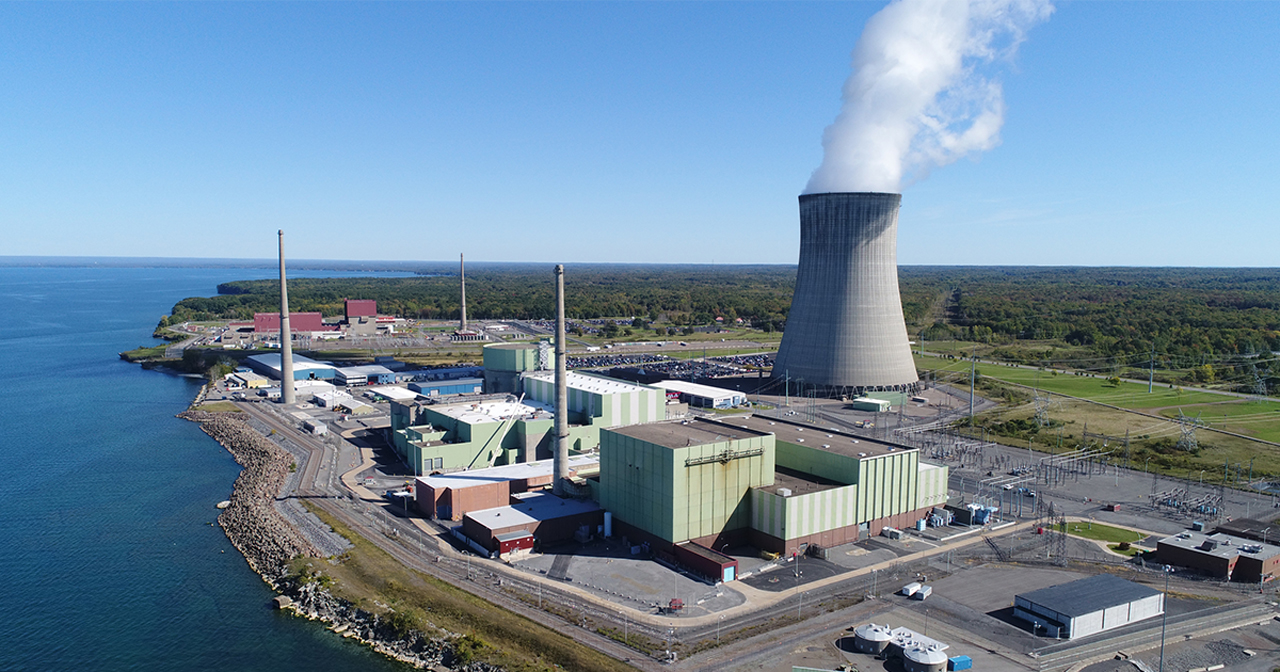
Constellation’s Nine Mile Point nuclear power plant. (Photo: Constellation Energy)
A nuclear-powered hydrogen production facility has commenced operation at Constellation Energy’s Nine Mile Point plant, the company announced this week. The facility is the first of its kind in the United States to generate hydrogen using nuclear power, courtesy of the New York plant’s two boiling water reactors, the 620-MWe Unit 1 and 1,287-MWe Unit 2.
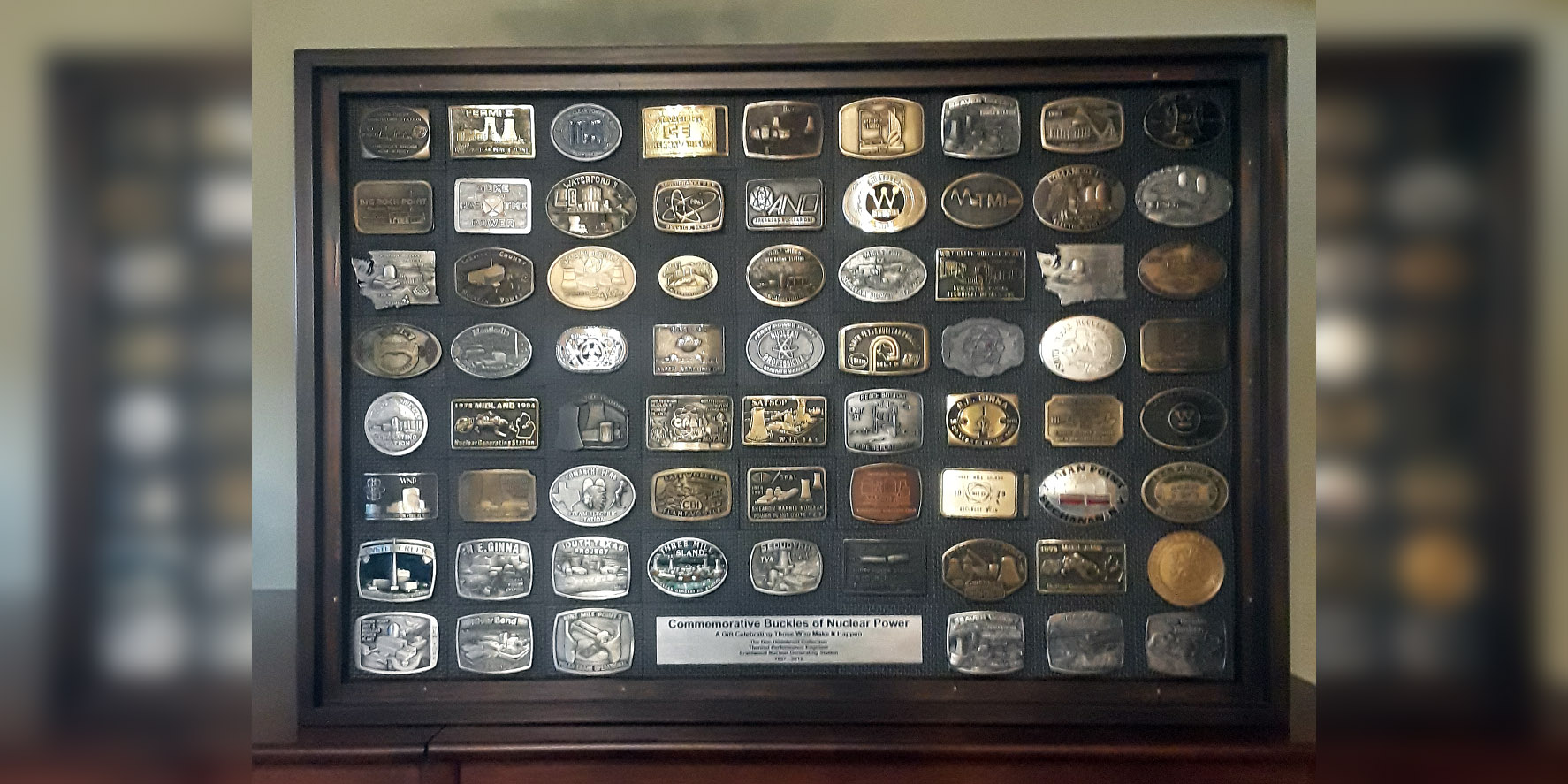
One of two cases that display the impressive belt-buckle collection.
Collecting belt buckles from nearly every nuclear power plant in the U.S. wasn’t the goal for Don Hildebrant when he obtained his first one. Over time, it just turned out that way.
One day years ago, Hildebrant came across a buckle from the nuclear plant where he worked, and it seemed before he knew it, he had collected more than 250 of them—some from plants that were never even completed. “When you look at the collection, you will see an interesting story of where nuclear power has been, and how far it has come,” he said.
What role will nuclear play in meeting clean energy goals?
The 2021 ANS Annual Meeting brought together three leading chief executive officers from the nuclear industry on June 16 for a discussion centered on the future role of nuclear energy deployment and the challenges of portfolio management during a time of net-zero carbon goals.
The plant’s Program Engineering Department head has overseen significant new technology implementations for maintenance.

The Zephyr system uses probes for steam generator inspections. Photos: APS
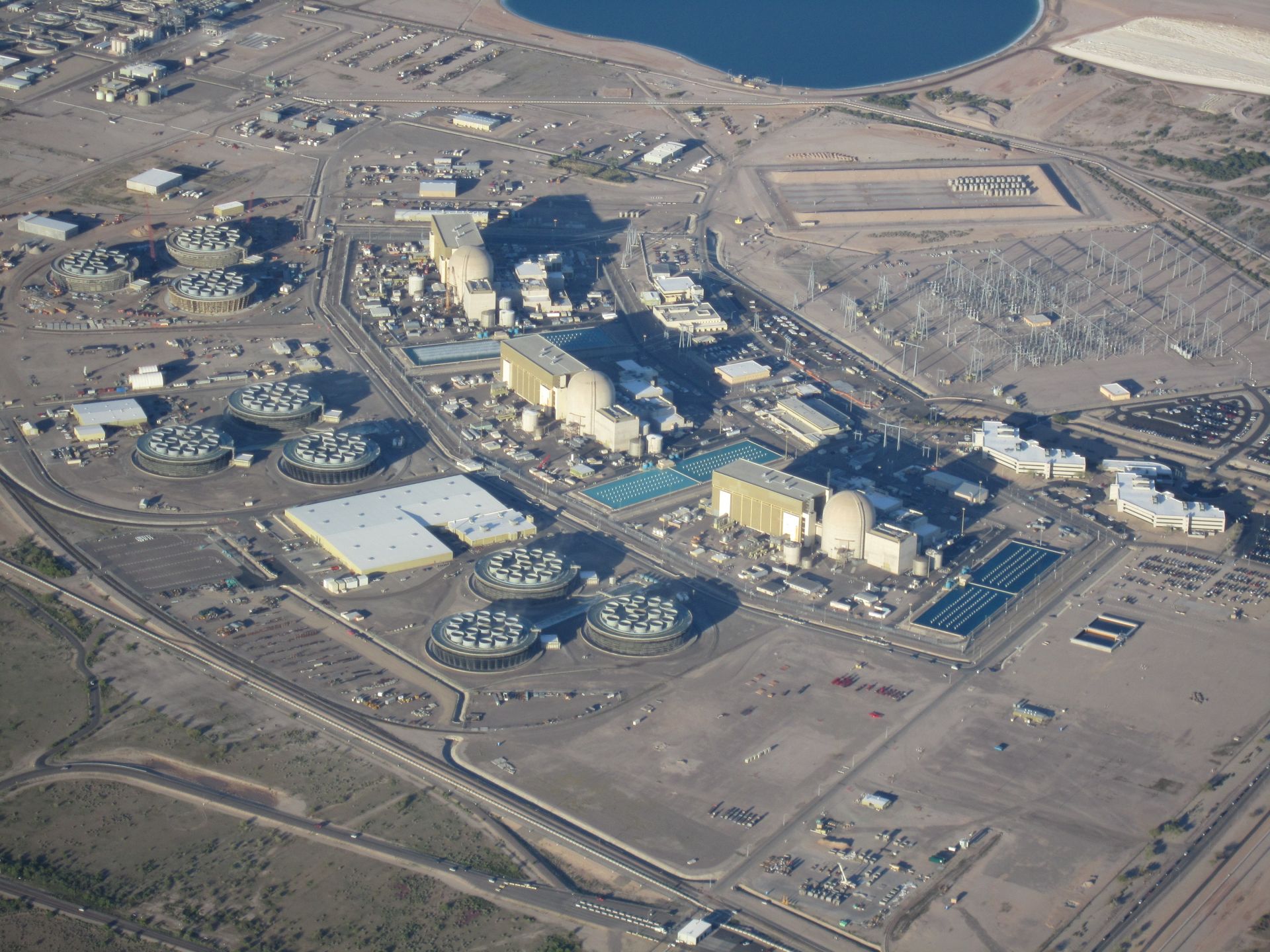
The Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station, a three-unit pressurized water reactor plant operated by Arizona Public Service Company, has started using an inspection technology relatively new to the nuclear industry. The technology, called smart pigs (an acronym for “piping inline gauges”), has previously been employed by oil and gas companies for inspecting and cleaning underground pipes. After testing and analyzing smart pig products from several companies, Palo Verde’s underground piping consultant, Dan Wittas, selected a smart pig suitable for navigating the tight-radius bends in the plant’s spray pond piping. The spray pond system consists of piping, a pump, and a reservoir where hot water (from the Palo Verde plant) is cooled before reuse by pumping it through spray nozzles into the cooler air. Smart pigs work by using the water’s flow through the piping to move an inspection tool within the pipe itself. The technology replaces the previous method of pipe inspection, in which various relatively small sections of piping were unearthed and directly inspected, and were considered to be representative examples of the overall piping condition. In contrast, the smart pigs obtain corrosion levels for the length of piping traveled through and allow a corrosion baseline to be established.